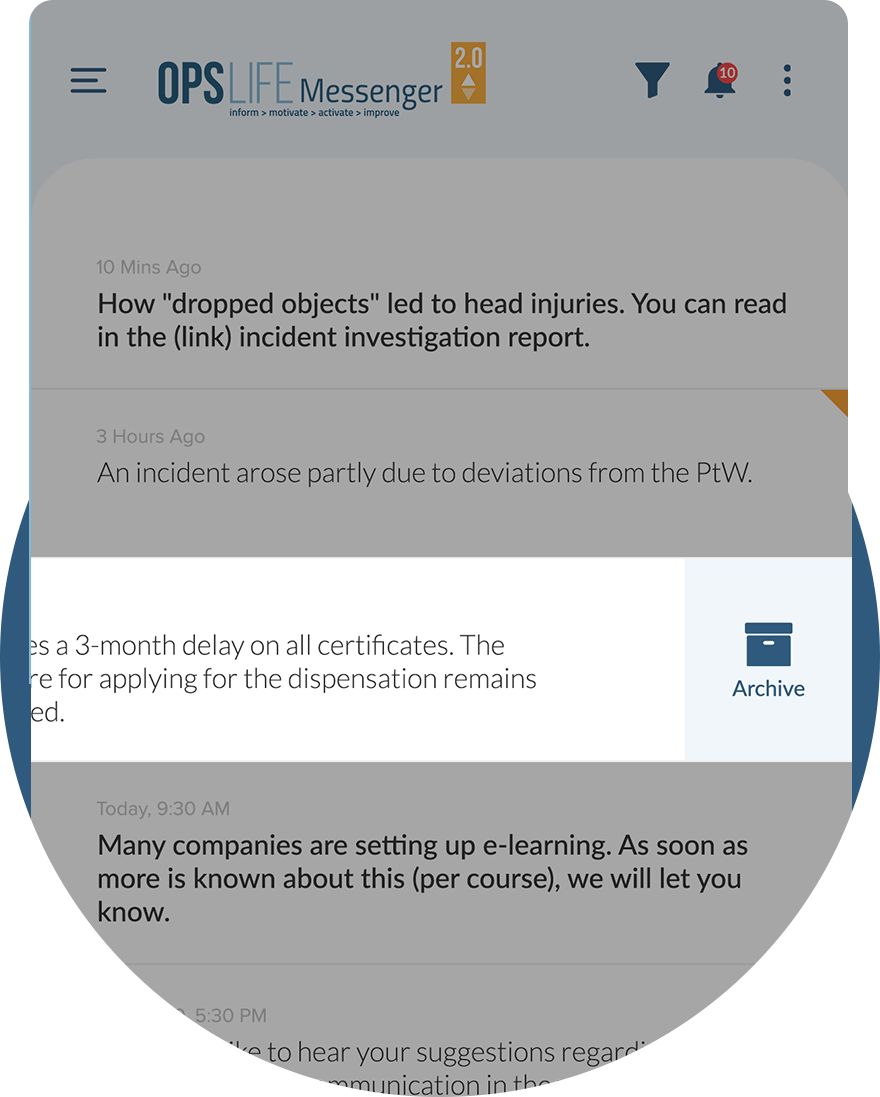
Basic HSE information about Dropped Objects and set of tools to be used at work
Dropped Objects
- Workplace Information
- Toolbox Information
- Check Your Knowledge
- Action Focus Campaign
IMPORTANT INFO
- Always wear hard safety helmets when work is being performed overhead or when other work conditions call for it.
- Secure tools and materials when working on an elevated surface.
- Cordon off hazard areas and post warning signs.
- Tools and safety equipment must always be inspected first before using.
- Communicate often; work as a team to avoid complacency and remain vigilant at all times.
WHAT IS IT?
The fall of a small, everyday object may seem relatively insignificant, especially if it falls from a low height. But no matter how small or ordinary such an object may be, such as a tape measure, a screw, a helmet, hand-held tools or wind-blown debris, if it falls from a sufficient height, it can develop enough velocity to cause serious injury or even death by the time it almost hits the ground.
Dropped objects are a major safety risk in the workplace. The heavier the object, the heavier the consequence. The farther it falls, the heavier the consequence.
Risks can be compounded by human error. Personnel working at height are at risk of dropping equipment. If these dropped objects strike another worker below, injury or possible fatality can occur. Dropped handheld tools and equipment constitute a prominent threat in numerous industries worldwide. Safety protocols are essential to help prevent falling objects.
Causes:
- poor maintenance
- poor hazard and risk assessment
- blind to the danger
- unnecessary/neglected material
- workplace clutter (housekeeping)
- scrap and waste left behind
- waste and excess material is not cleaned up
- lack of cleaning/inspection
- harsh weather conditions
- moving equipment
- strong vibrations
HAZARDS
Tools are essentially for workers at height to do their job. But they also pose risks to those below. The most common injuries workers suffer from falling objects are bruises, fractures, strains, and sprains. The objects that commonly fall range from large items such as steel beams to small items such as small hand tools.
Typical falling object hazards:
- loads falling from height during lifting and handling operations
- objects being dislodged during work at height
- objects falling from height because of adverse weather conditions, or wear and tear
- toppling of unstable objects
PREVENTION
There are two types of controls to prevent falling objects from hurting workers:
- physical controls physically stop the object from falling
- procedural controls refer to changing the way you work so that objects can’t fall
A few examples:
- secure tools and materials when working on an elevated surface to prevent them from falling on people below
- barricade hazard areas and post warning signs
- if you are performing work on open grating, place non-slip plywood or a similar product on top of the grating to prevent small objects from falling through it
- use toe boards, screens on guardrails or scaffolds to prevent falling objects
- use tool lanyards to prevent tools from falling
- keep all material at least 3 feet from a leading edge, other than material specifically required for work in process
- remove items from all loose or unsealed pockets, especially top shirt pockets, such as phones, pens, and tools
- do not hang objects over guardrails
- ensure toe boards are in place and inspected frequently
- require hard safety helmets and other required Personal Protective Equipment for every person in areas at risk for falling objects
- cordon off the area, if possible, where fall or drop hazards may exist
- inspect all Personal Protective Equipment prior to use to confirm it still meets manufacturers’ recommendations
- communicate often; work as a team to avoid complacency and remain vigilant at all times
PROTECTION
Basic equipment and work clothes must be used at all times. You may have to wear additional PPE, depending on the type of work. Ask your company about what to wear and when to wear it. The Permit to Work also states which basic and additional PPE you must wear. Always wear hard hats when work is being performed overhead or when other work conditions call for it.
Tools and safety equipment must always be inspected first before using. Uncertified tools and previously damaged tools are not allowed to be used.
IN CASE OF...
Unsafe working conditions should never be ignored and should always be kept in mind to avoid hazards. Regular inspection, repair, and maintenance are critical. It can help identify any possible damages and wear and tear in the workplace.
Start your daily work with safety!
Onscreen presentation is very useful to use during work preparation or toolbox meetings. It provides short and concrete information. Five questions and answers at the end of presentation can be used to make the meeting more interactive and to give conversation a boost.
Be always prepared for the work!
It is of utmost importance to be well prepared before you start the work.
By clicking on the button below you can check your knowledge about this HSEQ subject.
After completion of the knowledge check, your certificate will be visible in
MY ACCOUNT > My training.